Xanthan Gum Made From
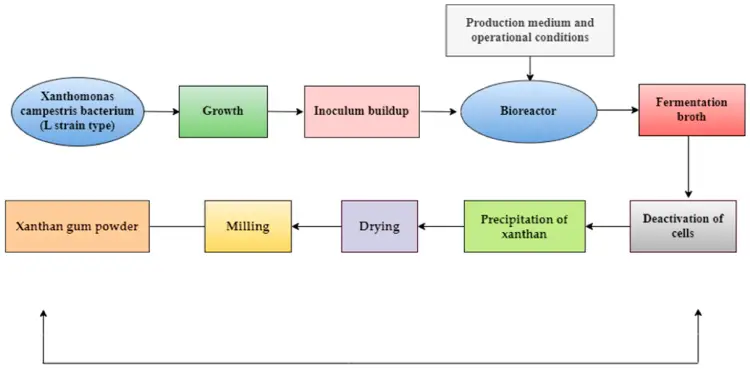
Xanthan gum is a popular food and industrial additive, known for its thickening and stabilizing properties. It is produced through the fermentation of sugars by a bacterium called Xanthomonas campestris. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how xanthan gum is made:
Source Material: The process begins with simple sugars derived from corn, wheat, soy, or other carbohydrate-rich sources. These sugars serve as the substrate for fermentation.
Fermentation Process: The bacterium Xanthomonas campestris is introduced to the sugar solution. As it ferments the sugars, it produces a viscous polysaccharide, which is xanthan gum.
Harvesting: After fermentation, the xanthan gum is separated from the mixture and purified.
Drying and Milling: The purified gum is then dried and ground into a fine powder, which can be used in various applications, from food to cosmetics and pharmaceuticals.
Uses of Xanthan Gum
Xanthan gum is a highly versatile and commonly used ingredient in the food industry. Its unique properties make it an essential additive in many food products, providing texture, stability, and consistency. Below are some of the key uses and benefits of food-grade xanthan gum:
1. Thickening Agent
Soups and Sauces: Xanthan gum is commonly used to thicken soups, gravies, and sauces. It helps create a smooth, consistent texture without altering the flavor of the product. Unlike traditional thickeners like cornstarch or flour, xanthan gum remains stable even under varying temperatures.
Beverages: It can also be used to thicken beverages, such as fruit juices or smoothies, giving them a rich, creamy texture.
2. Emulsifier and Stabilizer
Salad Dressings and Mayonnaise: Xanthan gum plays a key role in stabilizing emulsions, preventing the separation of oil and water phases. This is particularly important in salad dressings, mayonnaise, and other emulsified products where a uniform consistency is desired.
Ice Cream and Dairy Products: In ice cream and yogurt, xanthan gum prevents ice crystal formation, ensuring a smooth, creamy texture. It helps maintain product stability during freezing and thawing, making it ideal for frozen desserts.
Non-Dairy Alternatives: Xanthan gum is also used in plant-based milk (like almond or soy milk) and dairy-free creams to prevent separation and to maintain a smooth texture.
3. Gluten-Free Baking
Improves Texture: In gluten-free baking, xanthan gum is used to replicate the binding and elasticity properties of gluten, providing structure and chewiness to gluten-free bread, cookies, and cakes. It helps prevent the crumb from becoming dry or crumbly.
Moisture Retention: It helps retain moisture in gluten-free products, ensuring that they remain fresh and soft longer. Without xanthan gum, gluten-free baked goods tend to dry out more quickly.
4. Suspension Agent
Drinks and Liquid Foods: Xanthan gum can be used to suspend solid particles in liquid foods, such as in fruit juices, smoothies, or salad dressings. It helps prevent ingredients like pulp, fruit pieces, or seeds from settling at the bottom of the container.
Concentrated Juices: It is often used in fruit juices and flavored beverages to help maintain a uniform consistency and keep ingredients well-mixed.
5. Fat Replacer
Low-Fat and Reduced-Calorie Foods: Food-grade xanthan gum can be used in low-fat or reduced-calorie formulations to help simulate the creamy texture of fat without the calories. It adds thickness and mouthfeel to products like fat-free salad dressings, sauces, and dairy products.
6. Anti-Crystallization Agent
Frozen Desserts: In products like sorbets and ice cream, xanthan gum prevents the formation of large ice crystals, which can make the texture grainy. It helps to keep the dessert smooth, even when frozen for longer periods.
7. Clean Label Ingredient
Natural and Safe: As a naturally derived ingredient, food-grade xanthan gum is often preferred in clean label products. It is made through the fermentation of simple sugars using a bacterium called Xanthomonas campestris. It’s free from artificial chemicals, making it a safer choice for health-conscious consumers.



Benefits of Xanthan Gum
1. Versatile and Multi-Functional
Xanthan gum serves several functions in food processing, from thickening and stabilizing to emulsifying and suspending. This makes it a valuable ingredient in many types of food products.
2. Improves Texture
One of the main benefits of xanthan gum is its ability to improve the texture of food products. It helps provide a smooth, creamy, and consistent texture, which enhances the eating experience.
3. Gluten-Free
Xanthan gum is a crucial ingredient in gluten-free recipes, helping to replace the elasticity and structure that gluten provides in traditional baked goods. It improves the texture of gluten-free breads, cakes, and cookies, making them more appealing and less crumbly.
4. Stable in a Range of Conditions
Xanthan gum is highly stable across a wide range of temperatures, pH levels, and storage conditions. It doesn’t lose its effectiveness under varying environmental conditions, making it ideal for use in both hot and cold foods, as well as in frozen products.
5. Improved Shelf Life
By preventing ingredient separation and maintaining the texture of the product, xanthan gum helps extend the shelf life of many processed foods, keeping them fresher for longer.
6. Non-Allergenic
Xanthan gum is generally considered safe and non-allergenic, making it suitable for most people, including those with food sensitivities or allergies.
7. Natural and Safe
As a naturally derived ingredient, food-grade xanthan gum is safe for consumption and recognized as a safe food additive by regulatory agencies such as the FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) and EFSA (European Food Safety Authority).
8. Low Calorie and High Fiber
As a soluble fiber, xanthan gum contributes to the dietary fiber content of foods and may help improve digestive health, manage blood sugar levels, and contribute to a feeling of fullness.



If you would like to learn more about Xanthan Gum, including its price, uses, production process, technical specifications, and applications across various industries, feel free to contact us or leave a message. We are dedicated to providing you with professional advice and services.
